Problem/objective
Problem
Due to the essential maintenance and modernization of existing structures and infrastructure, the German national economy has to bear extraordinary high costs with an increasing tendency. A major part of the construction volume are steel constructions. Those very often are stressed by dynamic or changing stresses and strains. As an example, bridges, cranes and wind-energy plants can be mentioned. Those constructions’ service life is predominantly determined by fatigue strength of critical groove details. This implies that an improvement of those details’ fatigue strength leads to an enhancement of the overall construction’s service life.
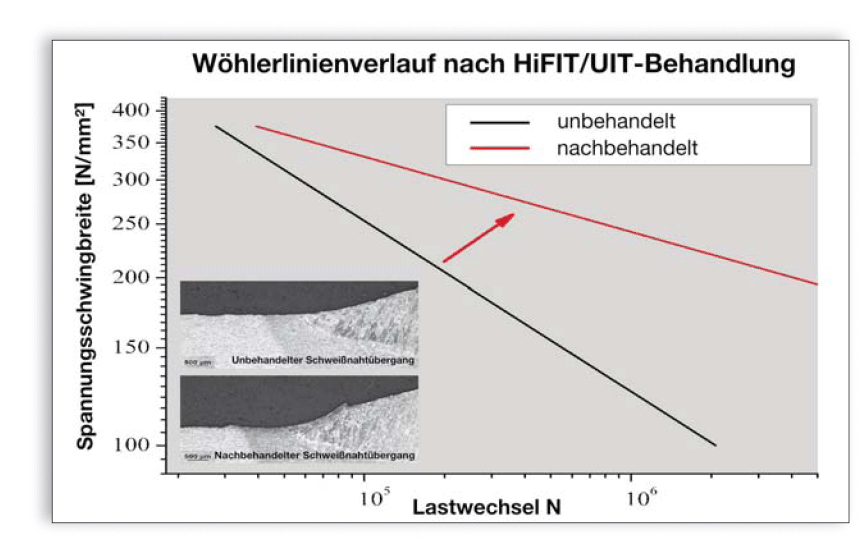
Nowadays the most used joining method for steel constructions is welding. Contrary to the many positive joining aspects the formation of weld seams intensely reduces the fatigue strength of the joined building parts. One possibility to reduce that disadvantageous effect, which implies a considerable service life reduction of alternate loaded constructions and therefore a significant charge of the national economy, are the methods of post weld treatments. Some of them already are applied in mechanical engineering with good results. A prerequisite for a broad implementation of life time expanding methods, especially in civil engineering, is that they become a part of a holistic concept. This means that, additionally to the application of life time expanding methods of existing and new constructions, methods for calculation and quantification of achievable effects as well as adequate quality assurance systems have to be provided. Such a holistic concept has to represent the whole life cycle from production to utilization to maintenance. Applications, influences as well as limits of the methods have to be approved as state of the art and base on extensive statistically confirmed examinations and have to be part of adequate guidelines.
Objective
The objective of REFRESH is to verify the effectivity of high-frequency post treatments for increasing the fatigue strength of existing and freshly welded steel constructions and to develop a holistic concept for the optimum use, the supervision and the consideration of those treatments in designing. This shall be realized by inclusion of suppliers and operators as well as accredited test centers. Based on substantiated preparatory work and inspections, an acceptance of methods to be developed by the relevant certification authorities shall be realized, that they will be considered valid in rules and standards.In the examinations’ focus are the promising high-frequency hammering post weld treatment methods. The influencing factors of those methods will be analyzed and optimized by the suppliers Dynatec GmbH and Applied Ultrasonics.
The quality assurance shall be accomplished by the inspection of effects close to edged layers. As a measurement method LKT GmbH’s micromagnetic methods will be enhanced to an on site quality assurance system. During the processing parameters’ enhancement the requirements of the involved operators will be included at an early stage.
The verification of the methods’ effectiveness and their related effects to the microstructures close to the edged layers as well as the building parts’ fatigue strength will be done by independent research facilities, the Institut für Bauwerkserhaltung and the Versuchsanstalt für Stahl, Holz und Steine.
With the development of a calculation method based on finite elements method, a consideration of fatigue strength enhancing effects will be possible for designing building parts with different groove details.
The broad range of operators allows market-oriented, fundamental preparatory work for a broad implementation of those methods after the project is completed. For this reason certification authorities in particular will be integrated at an early stage.