|
Following influences are to be examined:
- Influence of the hole diameter on the shear-carrying capacity
- Influence of the clamping thickness on the bearing of hole carrying capacity on supported and non supported connections
- Influence of the shell forming
The results can be summarized with the numerical data for the examined parameter range in the following way:
- To avoid the mode of failure of drawing under shear force on calculational failing systems by shearing, the drill hole diameter regarding the shell diameter dHü = d2 is to be limited to
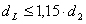
This is valid for steel construction anchors with a geometry that is equal or similar to the systems used in the test
- The hole clearance has predominant influence on the displacements and not that much on torsion. The displacements under service load with the highest acceptable hole clearance (dL = 1,15 dHü) account up to 2,5 times the value of the displacement of the connection with the lowest checked hole clearance. The torsions show consistent values in between 3° and 6°. Below the service load level, differences of torsion might occur, depending on if the bearing behavior is dominated by shearing or bearing of hole.
- The bearing of hole carrying capacity correlates with the bearing of hole carrying capacity of the screwed connections. The regulations in [1] and [4], regarding the bearing of hole carrying capacity, should be replaced by the regulations of DIN 18800-1:1990-11, whereas the upper limit al £ 2,0 for exterior and al £ 3,0 for interior building parts should be kept valid.
- If, alternatively, the regulations of DIN EN 1993-1:2007-05 for calculating the bearing of hole carrying capacity will be used, the roof should be made according to DIN EN 18800-1:1990-11, element (807) in the following way:
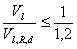
- The shell formation has no influence on the carrying capacity or on the forming behavior of the connection. It cannot be assumed, that a rubber ring has any negative influence on the carrying capacity or the forming behavior.
- Connections with anchors lead to bigger displacements in the joint section compared to connections with screws. This primarily is caused by bigger torsions. A negative influence on the carrying capacity does not exist though.
|
