Hybrid grout connections for steel structures (HybridGrout, P 1307)
- contact:
- project group:
Füge- und Klebtechnik
- funding:
FOSTA, AiF
- Partner:
Fraunhofer IFAM, Klebtechnik und Oberflächen
- startdate:
2018 - 2021
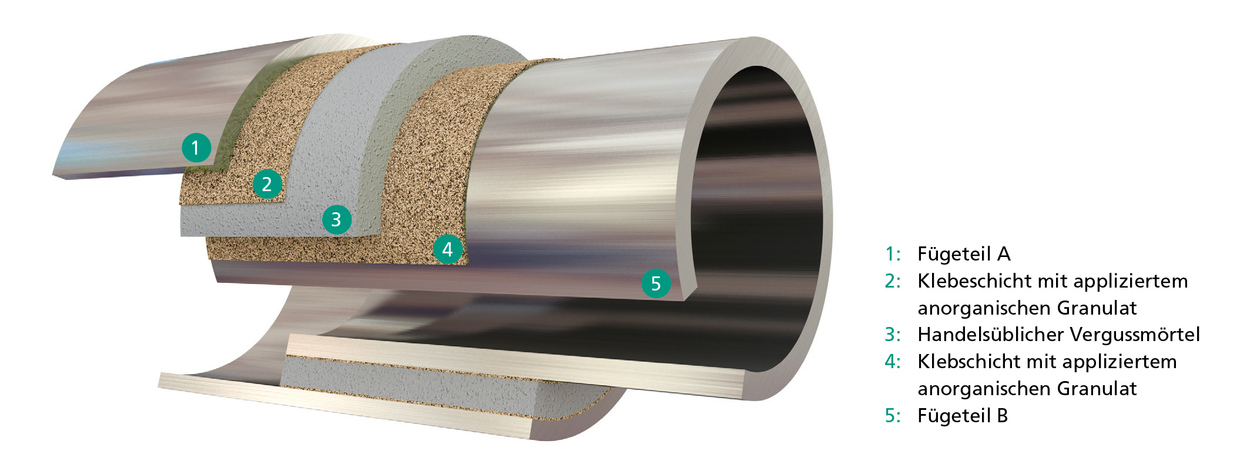
Grout joints are used for the production of push-in pipe connections, for example in the construction of foundation structures for wind turbines. The cylindrical joint gap, which is specifically dimensioned in its joint width to compensate for component tolerances, is grouted with a high-strength fine-grain mortar.
During the inspection of grouted monopile joints, however, considerable relative displacements of the joined components were frequently found, which could be attributed to a loss of the adhesive bond. To improve the interlock, mechanical thrust ribs are welded onto the surfaces of the joined parts. However, the weld seams represent starting points of fatigue cracks, a concentrated load application in the area of the thrust ribs damages the grout.
The aim of the research project is the systematic investigation of a novel grout joint. This joint consists of several layers: Thin layers of structural adhesives provide the adhesion to the joint surfaces. At the same time, the adhesive seals the steel surfaces and has an anticorrosive effect. The bond between the adhesive layer and the grout is achieved by means of an interspersed granulate. These production steps can be carried out in advance under controlled conditions in the manufacturing plant. Finally, the actual bond is created in situ with grout. Tests show a high load bearing capacity of the hybrid connection with very low scatter of the test results. The hybrid connection can represent an efficient and economical alternative to the usual joining methods of welding and bolting and can be used in many areas of application in steel construction.
In detail, the following focal points of investigation are set:
- Selection and characterization of suitable organic (structural adhesives) and inorganic (grouting mortar, bedding granules) materials for joint gap filling.
- Detailing and optimisation of the design of the joint geometry and the manufacturing concept
- Experimental investigation of the load-bearing and failure behaviour of the hybrid grout joint under static and fatigue loading as well as after dislocation
- Development of a design model for the design of hybrid grouted connections as well as validation of the computational model on the basis of large-scale component tests

